Introduction: Why Enterprises Must Move Beyond EJBs
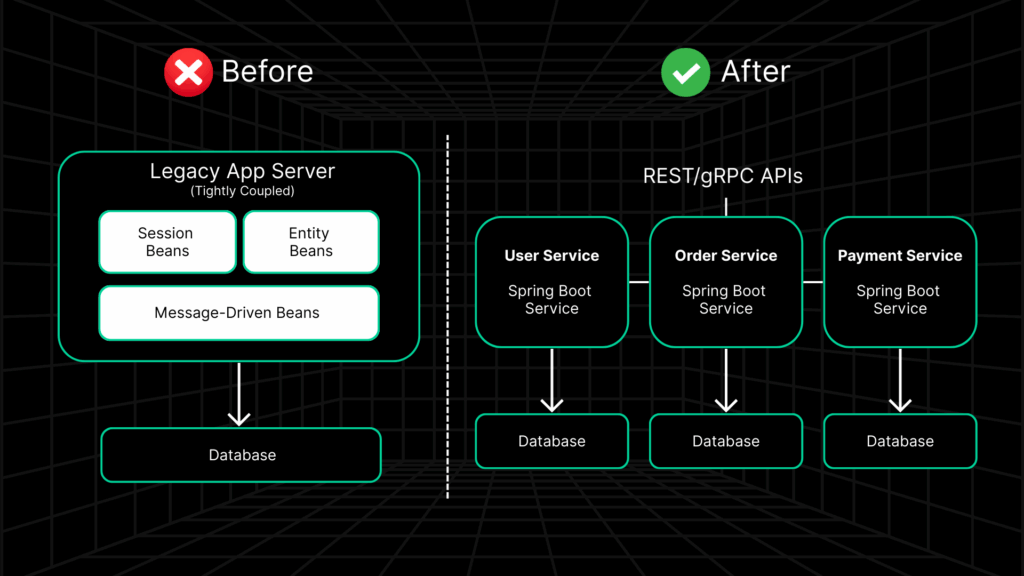
Enterprise Java Beans (EJBs) were once the backbone of large-scale enterprise applications, offering transaction management, security, and persistence. But in 2026, they have become a liability:
- Complex and rigid: Developers must work within heavyweight container-managed services.
- Performance bottlenecks: Distributed EJBs often lead to excessive remote calls and brittle coupling.
- Deployment drag: EJB-based systems depend on legacy app servers like WebLogic and JBoss, slowing down delivery pipelines.
- Cloud incompatibility: EJBs were not designed with microservices, containers, or Kubernetes in mind.
Spring Boot microservices offer a modern, lightweight alternative, enabling modular applications with improved agility, scalability, and cost efficiency.
What Spring Boot Microservices Bring to the Table
| Capability | EJBs (Java EE) | Spring Boot Microservices |
| Architecture | Monolithic, container-managed beans | Modular, independently deployable services |
| Footprint | Heavy app servers (WebLogic, JBoss) | Embedded servers (Tomcat/Jetty) |
| Scalability | Vertical scaling, expensive hardware | Horizontal scaling, container-native |
| Developer Productivity | Verbose, XML-heavy configs | Convention-over-configuration, annotations |
| Cloud Readiness | Poor fit for Docker/Kubernetes | Optimized for CI/CD pipelines and containers |
For CTOs and enterprise architects, Spring Boot microservices mean faster delivery, easier scaling, and long-term maintainability.
Also read: A Complete Java Migration Guide for Modernizing Legacy Enterprise Stacks.
Migration Challenges and Strategies
Moving from EJBs to Spring Boot isn’t a drop-in replacement. Common challenges include:
- Session Beans: Must be refactored into Spring-managed services.
- Entity Beans: Require re-mapping into JPA/Hibernate entities under Spring Data.
- Transaction Management: Shifting from container-managed to Spring’s @Transactional model.
- Remote Calls: Distributed EJB invocations must be re-architected into REST/gRPC endpoints.
- Security: Legacy JAAS-based configurations need to be modernized into Spring Security.
A refactoring-first migration strategy works best: incrementally replacing EJBs with Spring services while ensuring compatibility through patterns like Strangler Fig.
Why Gen AI Changes the Migration Playbook
Traditional migration methods involve large teams manually rewriting code, with high risk of introducing bugs. Gen AI-driven modernization flips the equation:
- Automated dependency tracing: AI parses millions of lines of code to identify every EJB reference and dependency.
- EJB → Spring service mapping: Stateless/Stateful session beans → Spring @Service or @Component classes; Entity beans → Spring Data JPA.
- Refactoring with guardrails: Compiler validation ensures AI-generated transformations compile cleanly and meet enterprise standards.
- Test generation: Automated unit and regression tests validate that new microservices behave identically to legacy EJBs.
This approach reduces manual effort by up to 70% while improving predictability and delivery timelines.
Also read: How Can Gen AI Drive Every Step of Your Modernization Journey?
Legacyleap in Action: Verified Modernization Outcomes
Legacyleap was purpose-built for this exact scenario: untangling fragile EJB-based systems.
- Full-system comprehension: Graph-based modeling captures every EJB relationship before migration.
- In-enterprise execution: Runs inside client environments, meeting compliance and regulatory requirements.
- Human-in-the-loop governance: AI outputs are always reviewed, approved, or refined by engineers.
- Beyond code refactoring: Auto-generates REST contracts, test suites, and container deployment manifests.
Also read: Why Legacyleap Is Your AI Companion Platform for Enterprise-Scale Modernization.
Measurable outcomes:
- 100% coverage of EJB dependencies mapped upfront.
- 70% automation in EJB → Spring Boot refactoring.
- 90%+ functional parity validated through AI-generated regression tests.
- Predictable delivery timelines, cutting modernization programs from years to months.
Conclusion: A Verified Path to Spring Boot Microservices
EJB-heavy applications are a ticking time bomb for enterprises as they are brittle, expensive, and unfit for modern cloud environments. Spring Boot microservices are the clear alternative, enabling agility and long-term maintainability.
But getting there requires more than brute-force rewrites. With Legacyleap’s Gen AI-powered platform, migration becomes faster, safer, and verifiable, ensuring functional parity, predictable timelines, and enterprise-grade governance.
Start with a $0 Assessment to map your EJB dependencies, evaluate migration feasibility, and see a verified modernization path tailored to your enterprise.
FAQs
Spring Boot microservices are lightweight, scalable, and cloud-native, while EJBs are rigid, costly, and tied to legacy app servers.
Yes. A refactoring-first approach transforms EJBs into Spring services incrementally, avoiding risky full rewrites.
Gen AI automates dependency tracing and refactoring, reducing manual work by up to 70% while ensuring compiler-verified code.
Transactions are mapped to Spring’s @Transactional model, ensuring business logic is preserved.
By auto-generating regression tests and validating outputs against enterprise coding standards, Legacyleap ensures modernized systems behave exactly like their EJB-based predecessors.